This tutorial shows how least Squares problems for matrices from ViennaCL or Boost.uBLAS can be solved solved.
We start with including the respective header files:
#define VIENNACL_WITH_UBLAS
#include <iostream>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/triangular.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/vector.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/vector_proxy.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/matrix.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/matrix_proxy.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/lu.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/io.hpp>
The minimization problem of finding x such that 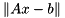 is solved as follows:
is solved as follows:
- Compute the QR-factorization of A = QR.
- Compute
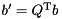 for the equivalent minimization problem
for the equivalent minimization problem 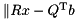 .
.
- Solve the triangular system
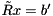 , where
, where 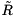 is the upper square matrix of R.
is the upper square matrix of R.
int main (
int,
const char **)
{
typedef boost::numeric::ublas::matrix<ScalarType> MatrixType;
typedef boost::numeric::ublas::vector<ScalarType> VectorType;
Create vectors and matrices with data:
VectorType ublas_b(4);
ublas_b(0) = -4;
ublas_b(1) = 2;
ublas_b(2) = 5;
ublas_b(3) = -1;
MatrixType ublas_A(4, 3);
ublas_A(0, 0) = 2; ublas_A(0, 1) = -1; ublas_A(0, 2) = 1;
ublas_A(1, 0) = 1; ublas_A(1, 1) = -5; ublas_A(1, 2) = 2;
ublas_A(2, 0) = -3; ublas_A(2, 1) = 1; ublas_A(2, 2) = -4;
ublas_A(3, 0) = 1; ublas_A(3, 1) = -1; ublas_A(3, 2) = 1;
Setup the matrix and vector with ViennaCL objects and copy the data from the uBLAS objects:
VCLVectorType
vcl_b(ublas_b.size());
VCLMatrixType vcl_A(ublas_A.size1(), ublas_A.size2());
Option 1: Using Boost.uBLAS
The implementation in ViennaCL accepts both uBLAS and ViennaCL types. We start with a single-threaded implementation using Boost.uBLAS.
std::cout << "--- Boost.uBLAS ---" << std::endl;
The first (and computationally most expensive) step is to compute the QR factorization of A. Since we do not need A later, we directly overwrite A with the householder reflectors and the upper triangular matrix R. The returned vector holds the scalar coefficients (betas) for the Householder reflections 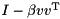
Compute the modified RHS of the minimization problem from the QR factorization, but do not form 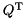 explicitly: b' := Q^T b
explicitly: b' := Q^T b
Final step: triangular solve: Rx = b'', where b'' are the first three entries in b' We only need the upper left square part of A, which defines the upper triangular matrix R
boost::numeric::ublas::matrix_range<MatrixType> ublas_R(ublas_A, ublas_range, ublas_range);
boost::numeric::ublas::vector_range<VectorType> ublas_b2(ublas_b, ublas_range);
std::cout << "Result: " << ublas_b2 << std::endl;
Option 2: Use ViennaCL types
ViennaCL is used for the computationally intensive BLAS 3 computations. Boost.uBLAS is used for the panel factorization on the host (CPU).
#define VIENNACL_WITH_UBLAS
#include <iostream>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/triangular.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/vector.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/vector_proxy.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/matrix.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/matrix_proxy.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/lu.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/io.hpp>
int main (
int,
const char **)
{
typedef boost::numeric::ublas::matrix<ScalarType> MatrixType;
typedef boost::numeric::ublas::vector<ScalarType> VectorType;
VectorType ublas_b(4);
ublas_b(0) = -4;
ublas_b(1) = 2;
ublas_b(2) = 5;
ublas_b(3) = -1;
MatrixType ublas_A(4, 3);
ublas_A(0, 0) = 2; ublas_A(0, 1) = -1; ublas_A(0, 2) = 1;
ublas_A(1, 0) = 1; ublas_A(1, 1) = -5; ublas_A(1, 2) = 2;
ublas_A(2, 0) = -3; ublas_A(2, 1) = 1; ublas_A(2, 2) = -4;
ublas_A(3, 0) = 1; ublas_A(3, 1) = -1; ublas_A(3, 2) = 1;
VCLVectorType
vcl_b(ublas_b.size());
VCLMatrixType vcl_A(ublas_A.size1(), ublas_A.size2());
std::cout << "--- Boost.uBLAS ---" << std::endl;
boost::numeric::ublas::matrix_range<MatrixType> ublas_R(ublas_A, ublas_range, ublas_range);
boost::numeric::ublas::vector_range<VectorType> ublas_b2(ublas_b, ublas_range);
std::cout << "Result: " << ublas_b2 << std::endl;
std::cout << "--- ViennaCL (hybrid implementation) ---" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Result: " << vcl_b2 << std::endl;
std::cout << "!!!! TUTORIAL COMPLETED SUCCESSFULLY !!!!" << std::endl;
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
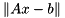 is solved as follows:
is solved as follows: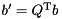 for the equivalent minimization problem
for the equivalent minimization problem 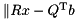 .
.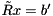 , where
, where 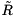 is the upper square matrix of R.
is the upper square matrix of R.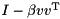
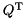 explicitly: b' := Q^T b
explicitly: b' := Q^T b