This tutorial explains the use of iterative solvers in ViennaCL.
- Note
- iterative.cpp and iterative.cu are identical, the latter being required for compilation using CUDA nvcc
We start with including the necessary system headers:
#include <iostream>
#ifndef NDEBUG
#define BOOST_UBLAS_NDEBUG
#endif
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/io.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/triangular.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/matrix_sparse.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/matrix.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/matrix_proxy.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/operation.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/operation_sparse.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/io.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/lu.hpp>
#define VIENNACL_WITH_UBLAS 1
A shortcut for convience (use ublas:: instead of boost::numeric::ublas::)
using namespace boost::numeric;
In the main() routine we create matrices and vectors using Boost.uBLAS types and fill them with data. Then, ViennaCL types are created and the data is copied from the respective Boost.uBLAS objects. Various preconditioners are set up and finally the iterative solvers get called.
Set up some ublas objects
ublas::vector<ScalarType> rhs;
ublas::vector<ScalarType> ref_result;
ublas::vector<ScalarType> result;
ublas::compressed_matrix<ScalarType> ublas_matrix;
Read system matrix from a matrix-market file
{
std::cout << "Error reading Matrix file" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
{
std::cout << "Error reading RHS file" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
{
std::cout << "Error reading Result file" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
Set up some ViennaCL objects
std::size_t vcl_size = rhs.size();
viennacl::copy(ref_result.begin(), ref_result.end(), vcl_ref_result.begin());
Transfer ublas-matrix to GPU:
An alternative way is to use the C++ STL. In such case, the sparse matrix is represented as a std::vector< std::map< unsigned int, ScalarType> > After the instantiation, the data from the uBLAS matrix is copied over to the STL-matrix, which is then copied over to a ViennaCL matrix. This step is just for demonstration purposes.
std::vector< std::map< unsigned int, ScalarType> > stl_matrix(rhs.size());
for (ublas::compressed_matrix<ScalarType>::iterator1 iter1 = ublas_matrix.begin1();
iter1 != ublas_matrix.end1();
++iter1)
{
for (ublas::compressed_matrix<ScalarType>::iterator2 iter2 = iter1.begin();
iter2 != iter1.end();
++iter2)
stl_matrix[iter2.index1()][static_cast<unsigned int>(iter2.index2())] = *iter2;
}
std::vector<ScalarType> stl_rhs(rhs.size()), stl_result(result.size());
std::copy(rhs.begin(), rhs.end(), stl_rhs.begin());
Set up ILUT preconditioners for ublas and ViennaCL objects:
std::cout << "Setting up preconditioners for uBLAS-matrix..." << std::endl;
std::cout << "Setting up preconditioners for ViennaCL-matrix..." << std::endl;
set up Jacobi preconditioners for ViennaCL and ublas objects:
Conjugate Gradient Solver
std::cout << "----- CG Method -----" << std::endl;
Run the CG method with uBLAS objects. Use a relative tolerance of 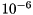 and a maximum of 20 iterations when using ILUT or Jacobi preconditioners. You might need higher iteration counts for poorly conditioned systems.
and a maximum of 20 iterations when using ILUT or Jacobi preconditioners. You might need higher iteration counts for poorly conditioned systems.
Run the CG method for ViennaCL objects. The results here should be the same as with uBLAS objects (at least up to round-off error).
Convenience option: Run the CG method by passing STL types. This will use appropriate ViennaCL objects internally. You need to include viennacl/compressed_matrix.hpp and viennacl/vector.hpp before viennacl/linalg/cg.hpp for this to work!
Stabilized BiConjugate Gradient Solver
std::cout << "----- BiCGStab Method -----" << std::endl;
Run BiCGStab for Boost.uBLAS objects. Parameters are the same as for the CG method.
Run the BiCGStab method for ViennaCL objects. The results here should be the same as with uBLAS objects (at least up to round-off error).
Convenience option: Run the BiCGStab method by passing STL types. This will use appropriate ViennaCL objects internally. You need to include viennacl/compressed_matrix.hpp and viennacl/vector.hpp before viennacl/linalg/bicgstab.hpp for this to work!
GMRES Solver
std::cout << "----- GMRES Method -----" << std::endl;
Run GMRES for Boost.uBLAS objects. Parameters are the same as for the CG method.
Run the GMRES method for ViennaCL objects. The results here should be the same as with uBLAS objects (at least up to round-off error).
Convenience option: Run the GMRES method by passing STL types. This will use appropriate ViennaCL objects internally. You need to include viennacl/compressed_matrix.hpp and viennacl/vector.hpp before viennacl/linalg/gmres.hpp for this to work!
That's it, the tutorial is completed.
std::cout << "!!!! TUTORIAL COMPLETED SUCCESSFULLY !!!!" << std::endl;
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Full Example Code
#include <iostream>
#ifndef NDEBUG
#define BOOST_UBLAS_NDEBUG
#endif
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/io.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/triangular.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/matrix_sparse.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/matrix.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/matrix_proxy.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/operation.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/operation_sparse.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/io.hpp>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/lu.hpp>
#define VIENNACL_WITH_UBLAS 1
using namespace boost::numeric;
{
ublas::vector<ScalarType> rhs;
ublas::vector<ScalarType> ref_result;
ublas::vector<ScalarType> result;
ublas::compressed_matrix<ScalarType> ublas_matrix;
{
std::cout << "Error reading Matrix file" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
{
std::cout << "Error reading RHS file" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
{
std::cout << "Error reading Result file" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
std::size_t vcl_size = rhs.size();
std::vector< std::map< unsigned int, ScalarType> > stl_matrix(rhs.size());
for (ublas::compressed_matrix<ScalarType>::iterator1 iter1 = ublas_matrix.begin1();
iter1 != ublas_matrix.end1();
++iter1)
{
for (ublas::compressed_matrix<ScalarType>::iterator2 iter2 = iter1.begin();
iter2 != iter1.end();
++iter2)
stl_matrix[iter2.index1()][static_cast<unsigned int>(iter2.index2())] = *iter2;
}
std::vector<ScalarType> stl_rhs(rhs.size()), stl_result(result.size());
std::copy(rhs.begin(), rhs.end(), stl_rhs.begin());
std::cout << "Setting up preconditioners for uBLAS-matrix..." << std::endl;
std::cout << "Setting up preconditioners for ViennaCL-matrix..." << std::endl;
std::cout << "----- CG Method -----" << std::endl;
std::cout << "----- BiCGStab Method -----" << std::endl;
std::cout << "----- GMRES Method -----" << std::endl;
std::cout << "!!!! TUTORIAL COMPLETED SUCCESSFULLY !!!!" << std::endl;
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
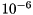 and a maximum of 20 iterations when using ILUT or Jacobi preconditioners. You might need higher iteration counts for poorly conditioned systems.
and a maximum of 20 iterations when using ILUT or Jacobi preconditioners. You might need higher iteration counts for poorly conditioned systems.